Overheating protection
Time:2021-09-07
Views:251
What is overheating protection
Overheating protection, as the name implies, is to activate the corresponding protection function when the temperature exceeds a certain threshold. Electronic devices will generate heat when they work, so most of them have overheat protection, and the protection will be activated when the corresponding threshold is exceeded [1]. For example: such as motor overheating protection, power device overheating protection, etc.
Continuously operating electromechanical equipment such as automatic lathes, electric ovens, ball mills, and other unattended equipment used in production, accidents caused by overheating or malfunction of the thermostat, must take corresponding protective measures.
principle
Generally, heat-sensitive electronic components are used to build an overheat protection circuit. When the temperature of the main circuit device is monitored by the thermal element, the temperature of the main circuit device rises to a certain value, the low-melting-point metal inside it will deform, which will push the main circuit to disconnect. , To achieve the purpose of protecting the main circuit equipment; after stopping for a period of time to dissipate heat, the thermal element monitors that the temperature of the main circuit equipment has dropped, and the low-melting-point metal inside it returns to its original shape, and the main circuit is connected, and the main circuit equipment is turned on again. Can work normally. [2]
Communication power supply equipment overheating protection
What is the form of overheating protection for communication power supply equipment that itself provides power to other equipment? There are two main ways.
1. When the temperature is too high, switch to other power supply equipment to supply power; when the temperature drops, the power supply resumes work, as shown in the figure.
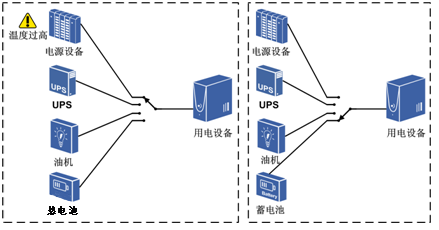
The temperature is too high, switch the power supply
2. When the temperature is not too high, improve the ventilation conditions inside the power supply and actively dissipate heat to the power supply, as shown in the figure.
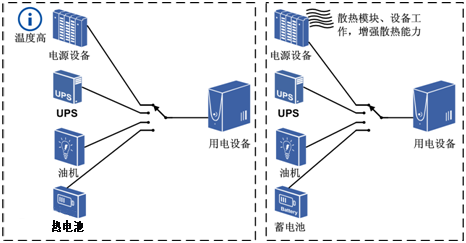
High temperature, improve heat dissipation





